Hough Voting
本文的标题是Deep Hough Voting,先来说一下Hough Voting。
用Hough变换检测直线大家想必都听过:对于一条直线,可以使用(r, θ)两个参数进行描述,那么对于图像中的一点,过这个点的直线有很多条,可以生成一系列的(r, θ),在参数平面内就是一条曲线,也就是说,一个点对应着参数平面内的一个曲线。那如果有很多个点,则会在参数平面内生成很多曲线。那么,如果这些点是能构成一条直线的,那么这条直线的参数(r, θ)就在每条曲线中都存在,所以看起来就像是多条曲线相交在(r,θ)。可以用多条曲线投票的方式来看,其他点都是很少的票数,而(r,θ)则票数很多,所以直线的参数就是(r,θ)。
所以Hough变换的思想就是在于,在参数空间内进行投票,投票得数高的就是要得到的值。
文中提到的Hough Voting如下:
A traditional Hough voting 2D detector comprises an offline and an online step. First, given a collection of images with annotated object bounding boxes, a codebook is constructed with stored mappings between image patches (or their features) and their offsets to the corresponding object centers. At inference time, interest points are selected from the image to extract patches around them. These patches are then compared against patches in the codebook to retrieve offsets and compute votes. As object patches will tend to vote in agreement, clusters will form near object centers. Finally, the object boundaries are retrieved by tracing cluster votes back to their generating patches.
对于这一段话的理解则是,已经有了一部分已经标注好的框和图片(或者feature),那么每一个框中的图片或者feature就相当于直线检测中的点,框相对于物体中心点的offset就相当于要vote的参数。在inference时,先选取一些RoI,然后将这些RoI或者其feature放入参数空间内,检索offset并且计算vote。具体的,也可以参考引文
VoteNet
本文要解决的核心问题是不同于2D Object Detection,3D 物体的中心往往离扫描到的点有一定距离,而且在空白处:
We face a major challenge when directly predicting bounding box parameters from scene points: a 3D object centroid can be far from any surface point thus hard to regress accurately in one step.
相对应Hough Vote,本文提出了VoteNet的网络结构,对Hough Vote做了如下的改进:
Interest points are described and selected by deep neural networks instead of depending on hand-crafted features.
Vote generation is learned by a network instead of using a codebook. Levaraging larger receptive fields, voting can be made less ambiguous and thus more effective. In addition, a vote location can be augmented with a feature vector allowing for better aggregation.
Vote aggregation is realized through point cloud processing layers with trainable parameters. Utilizing the vote features, the network can potentially filter out lowquality votes and generate improved proposals.
Object proposals in the form of: location, dimensions, ori- entation and even semantic classes can be directly generated from the aggregated features, mitigating the need to trace back votes’ origins.”
以上四部分都是针对Hough Vote做的改进,主要是使用神经网络进行兴趣点的选取,生成Vote,聚集Vote和生成框。
网络结构
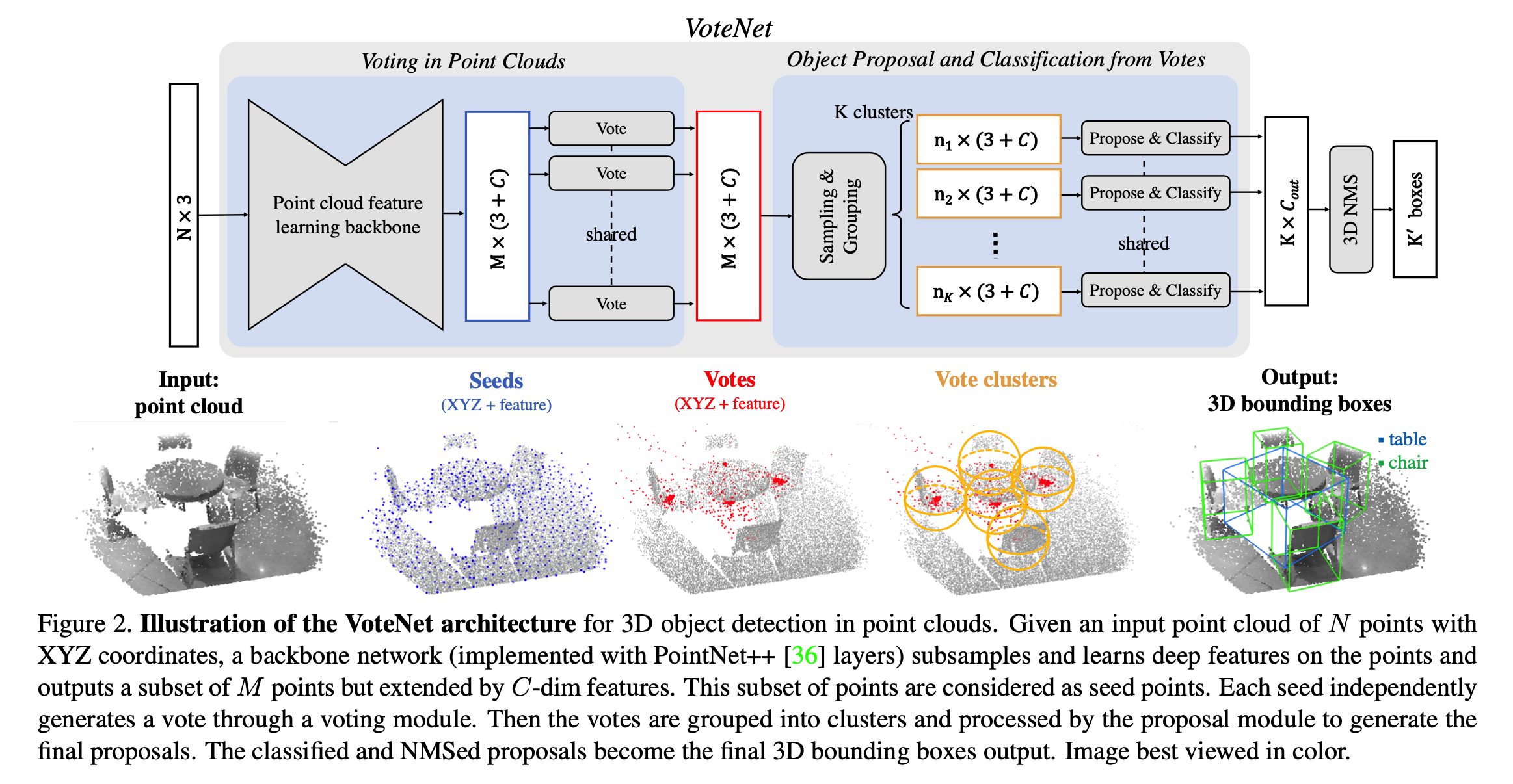
Voting in Point Clouds
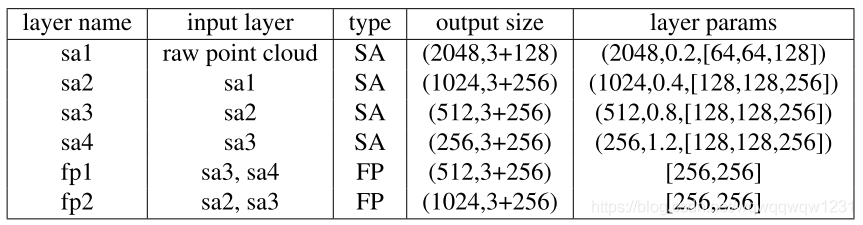
这部分就是PointNet++作为主干网络,包含4个SA层与2个FP层,得到 \(M \times (3 + C)\) 的Tensor,这个tensor表示着选出来的Seed和每个Seed对应的特征向量。那么主干网络具体的参数如下表,也就是M=1024,C=256。
Vote的过程其实就是使用MLP对Seed回归其对应中心的offset的过程。但在回归时,不仅回归其归属的物体的中心,而且回归一个feature的offset。那么这一块的结构文中提到:
“The voting module MLP has output sizes of 256, 256, 259 for its fully connected layers. The last fully connected layer does not have ReLU or BatchNorm.”
得到的位置的offset和feature的offset,element-wise的加到主干网络的输出上,更新Seed的位置和feature
Object Proposal and Classification from Votes
Sampling and Grouping
对Vote产生的Seed进行furthest sampling,然后按照一定距离内的进行Grouping操作。实验中验证了这个方式的有效性,距离在0.2时是最好的。
Proposal and Classify
对于Grouping得到的特征,送入到PoinNet中,进行一次MLP,然后MaxPooling操作得到特征向量,然后再进行一次MLP得到输出。令人疑惑的是,在正文中说第一个MLP是PointNet-like的形式,而在Appendix中则提到是SA结构的:
“The proposal module as mentioned in the main paper is a SA layer followed by another MLP after the max-pooling in each local region. ”
我认为PointNet的特殊之处是在MLP之前加入了T-Net,但SA module中则是使用相对位置做直接使用MLP的。这一块很疑惑,文中也没有解释太清楚。
第二层的MLP的输出的channel数为5 + 2 N H + 4 N S + N C 5+2NH+4NS+NC5+2NH+4NS+NC,是参考了FrustumNet的输出,文中解释为:
“The layer’s output has 5+2NH+4NS+NC channels whereNH is the number of heading bins (we predict a classification score for each heading bin and a regression offset for each bin–relative to the bin center and normalized by the bin size), NS is the number of size templates (we predict a classification score for each size template and 3 scale regression offsets for height, width and length) and NC is the number of seman- tic classes. In SUN RGB-D: NH = 12,NS = NC = 10, in ScanNet: NH = 12,NS = NC = 18. In the first 5 channels, the first two are for objectness classification and the rest three are for center regression (relative to the vote cluster center).”
代码结构
train.py
# train.py
# 具体的内容可以看源码,这里只是记录一些代码要干的事情,很有借鉴意义的代码。
1.通过parser定义trian过程需要的参数
2.定义Log_dir和Dump_dir,并打开Log_dir,写入本次训练的parser中有关config的参数
3.定义一个写入log的函数,只是在trian.py中调用
4.加载dataset的config,加载dataset,在定义dataset时,使用train和eval两种模式,甚至还可以55.加入test模式,从而可以共用dataset的接口
6.定义worker_init_fn,加载dataloader
7.加载model,并将其放到nn.DataParallel中
8.加载criterion,由于loss计算越来越复杂,定义一个函数或者类
9.定义optimizer
def train_one_epoch():
stat_dict = {} # 定义一个储存中间过程变量的dict
adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, EPOCH_CNT) # 调整lr
bnm_scheduler.step() # decay BN momentum
for batch_idx, batch_data_label in enumerate(TRAIN_DATALOADER):
前向计算
计算loss
反向传播
统计中间结果
展示中间结果
def eval_one_epoch():
相比于train_one_epoch,增加计算最终统计量的部分例如AP,其他相同
def trian():
for epoch in range(start_epoch, MAX_EPOCH):
log记录epoch的属性
np.random.seed()
train_one_epoch()
if EPOCH_CNT == 0 or EPOCH_CNT % 10 == 9: # Eval every 10 epochs
loss = evaluate_one_epoch()
# Save checkpoint
save_dict = {'epoch': epoch+1, # after training one epoch, the start_epoch should be epoch+1
'optimizer_state_dict': optimizer.state_dict(),
'loss': loss,
}
try: # with nn.DataParallel() the net is added as a submodule of DataParallel
save_dict['model_state_dict'] = net.module.state_dict()
except:
save_dict['model_state_dict'] = net.state_dict()
torch.save(save_dict, os.path.join(LOG_DIR, 'checkpoint.tar'))
if __name__=='__main__':
train(start_epoch)
训练数据处理
Sunrgbd的data是以matlab形式储存的,作者提供了从matlab中读出数据和label的函数:
- extract_split.m:将数据集分割成训练集和验证集
- extract_rgbd_data_v2.m:将v2版的label以txt形式储存,并且复制每个数据的depth,img和calib文件
- extract_rgbd_data_v1.m:将v1版的label以txt形式储存
在储存好上述数据之后,使用python sunrgbd_data.py --gen_v1_data进一步处理数据,将depth数据降采样,并构造votes的数据。
sunrgbd_data.py
Dumps:
<id>_pc.npz of (N,6) where N is for number of subsampled points and 6 is
for XYZ and RGB (in 0~1) in upright depth coord
<id>_bbox.npy of (K,8) where K is the number of objects, 8 is for
centroids (cx,cy,cz), dimension (l,w,h), heanding_angle and semantic_class
<id>_votes.npz of (N,10) with 0/1 indicating whether the point belongs to an object,
then three sets of GT votes for up to three objects. If the point is only in one
object's OBB, then the three GT votes are the same.
sunrgbd_detection_dataset.py
一个是需要注意的是point_votes的产生是在sunrgbd_data.py中产生的,这相当于一个前处理的过程,其描述如下:
<id>_votes.npz of (N,10) with 0/1 indicating whether the point belongs to an object,
then three sets of GT votes for up to three objects. If the point is only in one
object's OBB, then the three GT votes are the same.
也就是vote[0]表示该点在不在一个物体的内部,vote[1:4]、vote[4:7]、vote[7:10]表示该激光点与所属物体的中心的位置偏差。
接下来,我们解释一下ret_dict包含的变量所代表的含义,基本这些含义是从构建label的地方就能看懂:
- pointclouds:点云,最后一列代表减去地面高度的高度, (N,3+C) N=20000
- center_label:box中心的位置 ,(MAX_NUM_OBJ,3), MAX_NUM_OBJ=64
- heading_class_label:box朝向的class的label , (MAX_NUM_OBJ,) values in 0,...,NUM_HEADING_BIN-1
- heading_residual_label:box朝向residual的label, (MAX_NUM_OBJ,)
- size_class_label:box的whl的class的label, (MAX_NUM_OBJ,) values in 0,...,NUM_SIZE_CLUSTER
- size_residual_label:box的whl的residual的label, (MAX_NUM_OBJ, 3)
- sem_cls_label:box的semantic class的label, (MAX_NUM_OBJ,)
- box_label_mask:是指示在box_label中,哪些box是真正的,哪些是用零补, (MAX_NUM_OBJ)
- vote_label: votes, (N,9)
- vote_label_mask:指示某个点参不参与vote的计算, (N,)
- scan_idx
- max_gt_bboxes:指示box_label中真实的box的数量,也就是box_label_mask相加
train过程详解
使用end_points字典来储存中间变量,使得查看重要的变量非常方便。
网络分为backbone_net,vgen和pnet几个模块,分别如下:
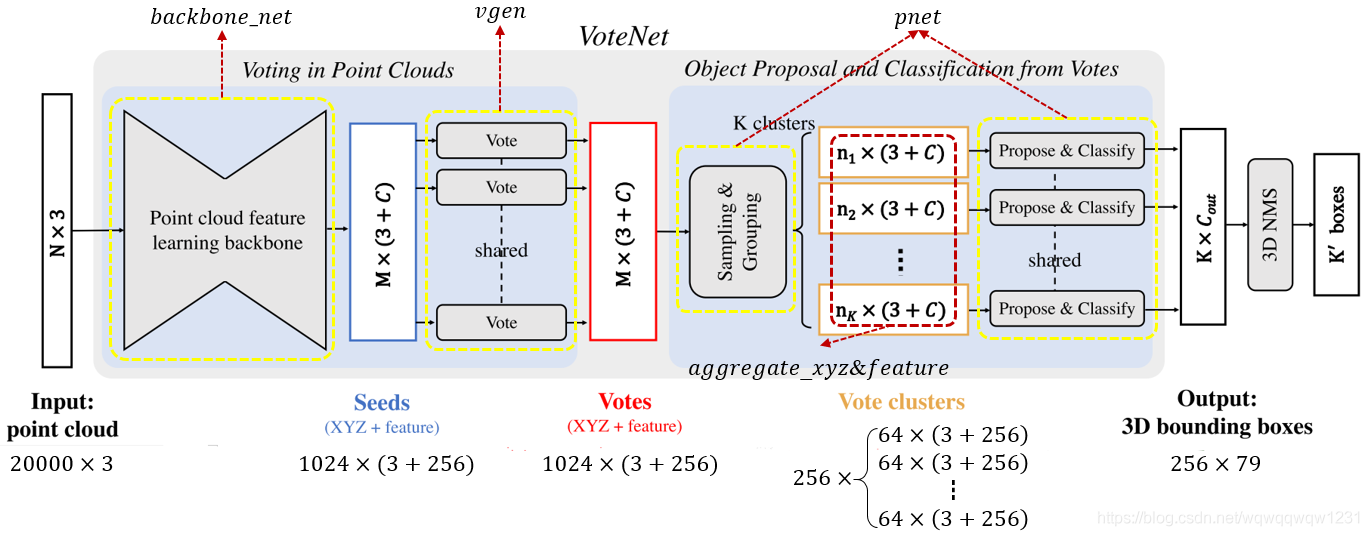
def forward(self, inputs):
""" Forward pass of the network
Args:
inputs: dict
{point_clouds}
point_clouds: Variable(torch.cuda.FloatTensor)
(B, N, 3 + input_channels) tensor
Point cloud to run predicts on
Each point in the point-cloud MUST
be formated as (x, y, z, features...)
Returns:
end_points: dict
"""
end_points = {}
batch_size = inputs['point_clouds'].shape[0]
end_points = self.backbone_net(inputs['point_clouds'], end_points)
# --------- HOUGH VOTING ---------
xyz = end_points['fp2_xyz']
features = end_points['fp2_features']
end_points['seed_inds'] = end_points['fp2_inds']
end_points['seed_xyz'] = xyz
end_points['seed_features'] = features
xyz, features = self.vgen(xyz, features)
features_norm = torch.norm(features, p=2, dim=1)
features = features.div(features_norm.unsqueeze(1))
end_points['vote_xyz'] = xyz
end_points['vote_features'] = features
end_points = self.pnet(xyz, features, end_points)
return end_points
前向计算过程
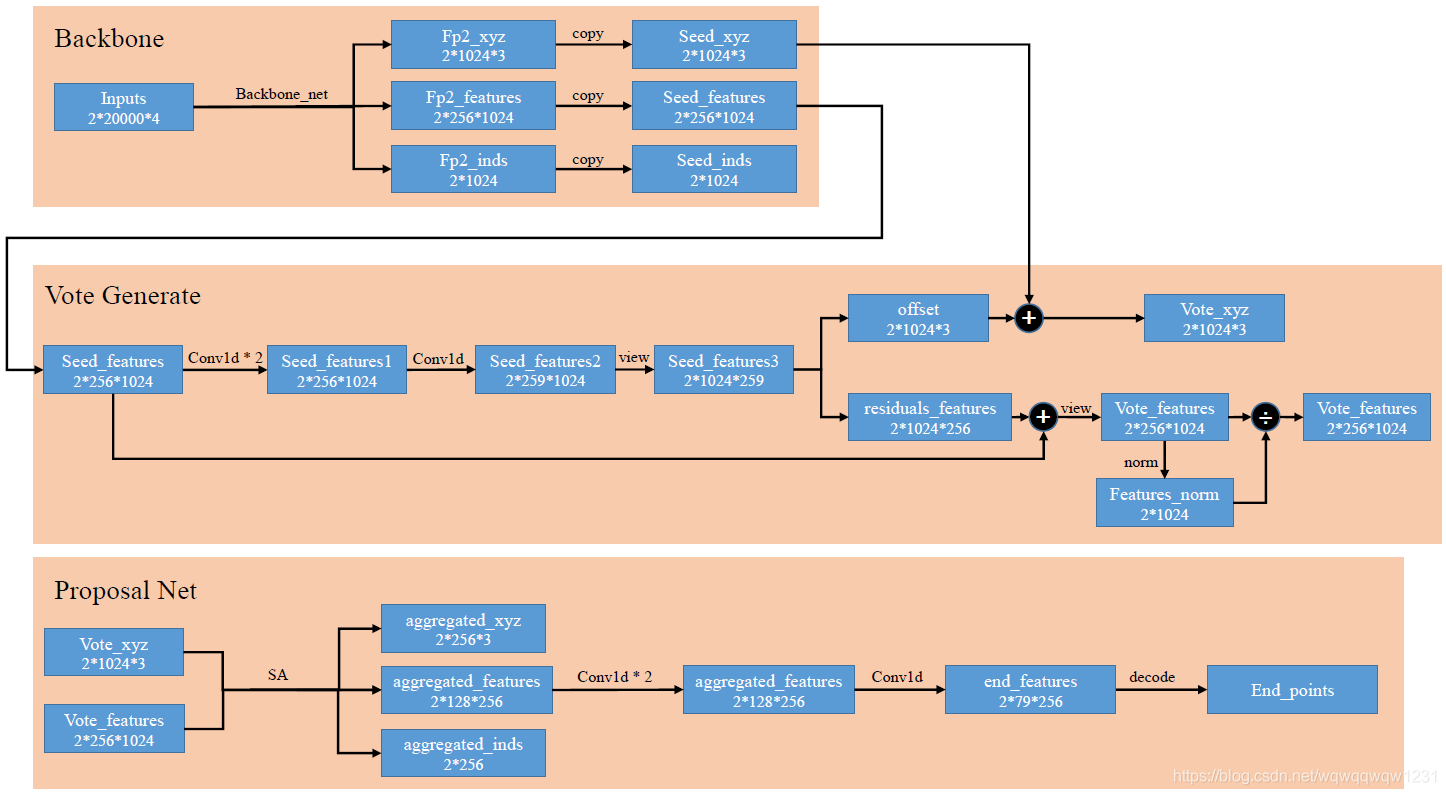
具体的前向计算过程如上图:
- Backbone:BackBone由Pointnet++构成,包括4层SA层,2层FP层,最终输出的Seed_inds是指示Seed_xyz在Inputs中的位置。
- Vote Generate:对Seed_features使用Conv1d得到vote的offsets和residuals_features,然后与seed的xyz和feature相加,得到vote_xzy和vote_features,最后对vote_features进行归一化。(这个归一化在文中并没有提到啊?)
- Porposal Net:对Vote_xyz和Vote_feature再过一层SA,然后对feature使用Conv1d得到最终结果,通过decode构建计算loss的变量。
Backbone
PointnetSAModuleVotes
- input:
- FurthestPointSampling: Uses iterative furthest point sampling to select a set of
npointfeatures that have the largest minimum distance. xyz(B,N.3)→fps_inds(B, npoint) - GatherOperation: xyz(B,N,3), fps_inds(B,npoint) → new_xyz(B,npoint,3)
- QueryAndGroup:xyz, new_xyz, features → new_features(B, 3 + C, npoint, nsample)
- mlp: conv(1x1)→bn→relu
- pooling: maxpooling(1xnsample)→ new_features (B, mlp[-1], npoint)
PointnetFPModule
- input:
- three_nn:Find the three nearest neighbors of unknown in known unkown(B,n,3), known(B,m,3)→ dist(B, n, 3), idx(B, n, 3)
- ThreeInterpolate:known_feats(B,C2,m), idx(B,n,3),weight(B,n,3) → interpolated_feats(B,C2,n)
- mlp: concat(interpolated_feats,unknow_feats)→ conv(1x1)→bn→relu
vgen: VotingModule
```plain text
seed_xyz: (batch_size, num_seed, 3) Pytorch tensor
seed_features: (batch_size, feature_dim, num_seed) Pytorch tensor
Returns:
vote_xyz: (batch_size, num_seedvote_factor, 3)
vote_features: (batch_size, vote_feature_dim, num_seedvote_factor)
- mlp(seed_features)→out(batch_size, (3+out_dim)*vote_factor, num_seed)
- out = [offset, residual_features]
- vote_xyz = seed_xyz + offset
- vote_features = seed_features + residual_features
## pnet:Proposal Module
```plain text
xyz: (B,K,3)
features: (B,C,K)
Returns:
scores: (B,num_proposal,2+3+NH*2+NS*4)
- vote_aggregation: PointnetSAModuleVotes (B, mlp[-1], num_proposal)
- mlp: →out (batch_size, 2+3+num_heading_bin2+num_size_cluster4, num_proposal)
- decode:net_transposed(B,num_proposal,2+3+num_heading_bin2+num_size_cluster4)
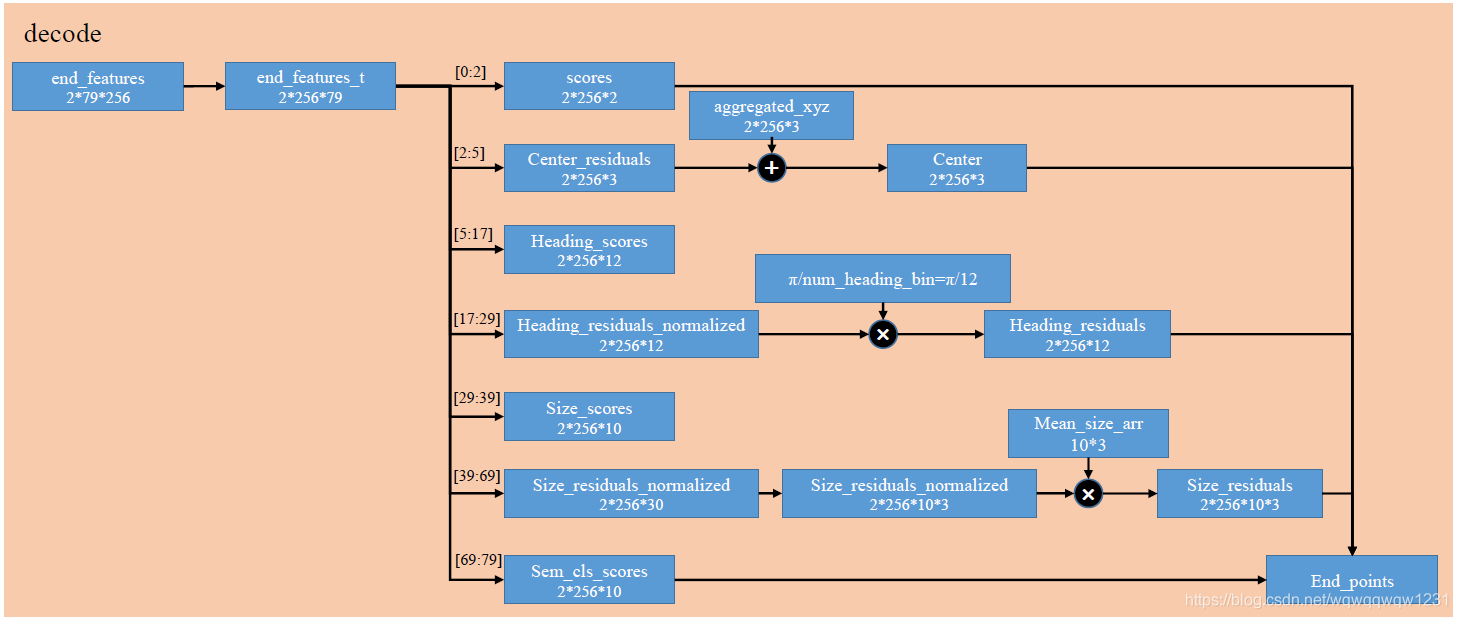
Decode过程不产生梯度,没有卷积层,只是把最终的结果解析成计算loss的变量
Loss
Loss的构成分为好几部分,比较复杂。
Vote Loss
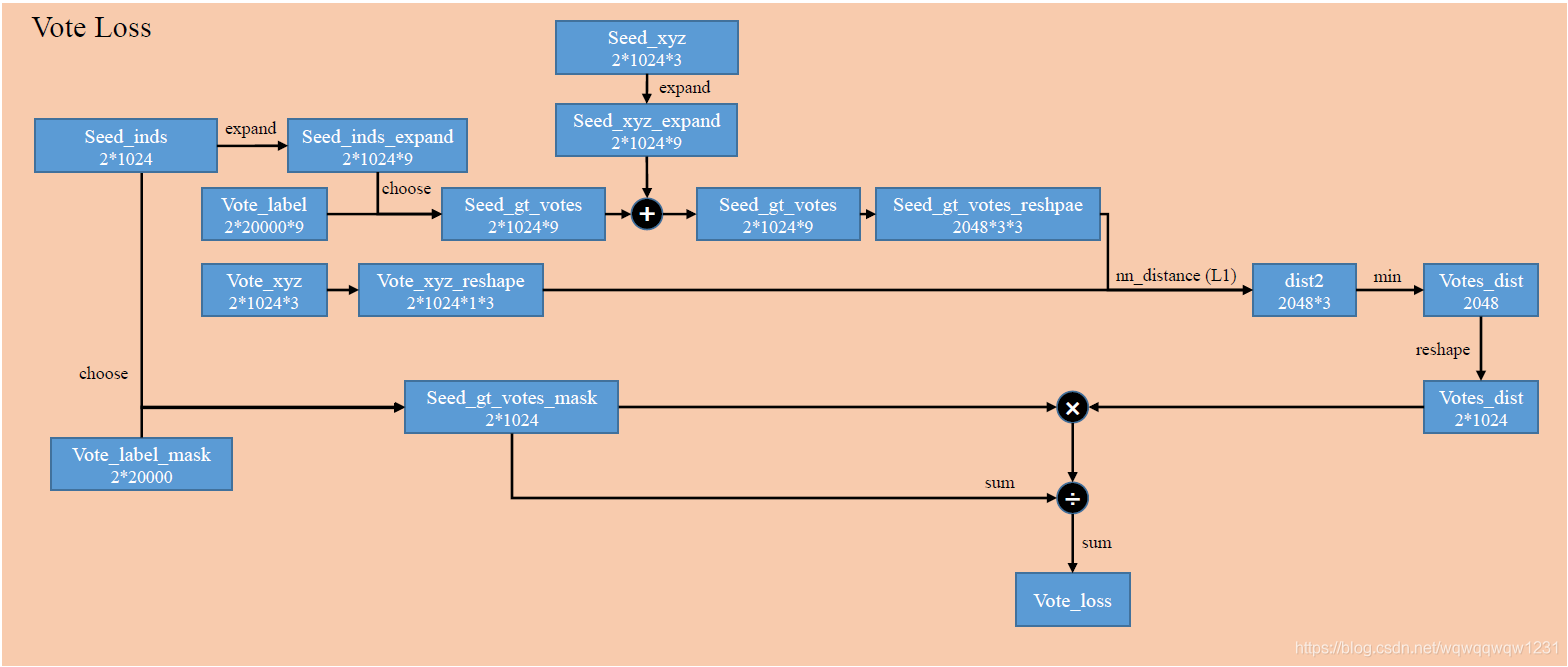
计算Vote与真值的差别,步骤如下:
- 根据Seed_inds从初始数据中的Vote_label中找到降采样后的Vote_label,然后加在Seed_xyz上得到Vote_xyz的真值,也就是Seed_gt_votes_reshape
- 通过nn_distance计算预测值与真值的差距。nn_distance的作用是计算两个储存位置信息的tensor之间的距离差,tensor A的维度为(batch,参与计算距离的点的数目,3)。所以该nn_distance是计算Vote_xyz_reshape中的一个点与Seed_gt_votes_reshape中的3个点计算距离,输出距离最小值,这样操作重复2048个点。L1表示是使用L1距离。所以dist2则是Seed_gt_votes_reshape中的3个点距离Vote_xyz_reshape中对应点的距离,然后取最小值得到Votes_dist。
- 通过Seed_inds选取mask,当seed点在物体内时,Vote_label_mask为1,其余为0,然后相乘则是使用mask使得不是物体内的点不参与loss的计算,相除是为了归一化